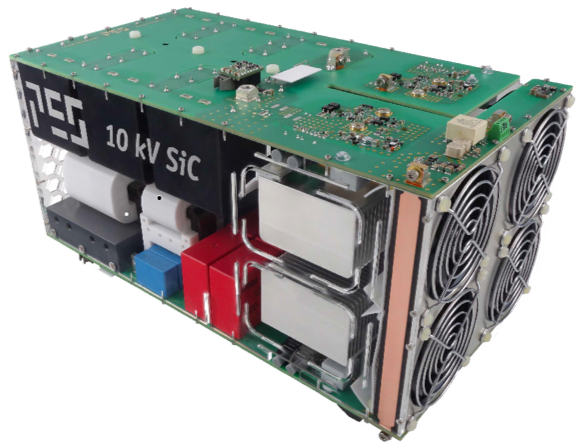
A solid-state transformer (SST) alternatively known as “smart transformer,” is a modern electrical energy device that offers bi-directional power flow. It is an amalgamation of high-powered semiconductor components, control circuitry, and conventional high-frequency transformers, offering reactive power compensation, harmonics reduction, and many others. Solid-state transformers cater to a wide variety of applications, ranging from alternative power generation to traction locomotives, power grid and electric industries, and others. Solid-state transformers are used in a wide range of applications, which would facilitate the smooth transition from AC to DC and DC to AC, besides voltage conversion. However, alternative power generation is the most dominant application of solid-state transformers. It provides an option for DC output of the required magnitude as well. In a typical solid-state transformer, the incoming voltage is converted into high-frequency AC with the use of a power electronic-based converter and then fed to the primary side of the high-frequency transformer. Many of the advantages with solid-state transformers come through reductions in size. Today, planting a transformer is not an easy task. Considerations like transportation, site preparation, installation, and transmission costs all add to the budget. By contrast, smaller, cheaper solid-state transformers could be relatively easily planted in small solar fields or storage pods. The faster switching speed of solid-state devices would in turn make it easier for a utility to handle a multiplicity of power sources feeding into the grid because you’d have more transformers controlling and fine-tuning power quality.
Solid State Transformer